Configs
The Configs menu handles the general configuration of Renoise.
"GUI" takes care of the Graphical User Interface you're working with,
"MIDI" handles the MIDI settings,
"Audio" is the section for everything that deals with your soundcard(s),
"Misc" (miscellaneous) deals with everything that doesn't below anywhere else (you'll find the VST setup here), and
"Keyb/Mouse" takes care of the things you can do with your keyboard and mouse.
Screen displays (from top-left to bottom-right)
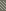
GUI (Graphical User Interface)
Hide 0's in effectcolumns
Enables/disables the display of unused effect commands.Framework
Enables/disables drawing of frames in pattern editor.Positionnumbers format
Choose hexadecimal or decimal pattern line numbers here.Highlight every x Lines
Sets how often line highlighting will be displayed.
4 is recommended for standard 4/4 measure.Pattern font
Choose your favorite pattern font here.ColorSettings
Choose your favorite colors for the GUI here. All interface
parts are selectable via the bottom fields, and for all parts you have the
three RGB (red/green/blue) sliders with values from 0 to 255.
Saving your favorite theme is possible by selecting "Skin" in the DiskOp menu,
entering a name on the right side of it and clicking "Save".Knob shade
Amount of 3D shading effect (on buttons)Body shade
Amount of 3D shading effect (on panels)Antialias
Amount of smoothing of font edgesFull Screen Resolution
The screen resolution Renoise will use when
switched to full screen mode
MIDI

MIDI Input
The available MIDI In Devices/drivers for devices like MIDI keyboards
etc. are automatically detected during the startup of Renoise. Choose your favorite
one here.Rec Note Off/Velocity/Prg Change/Controller
These options define what kinds of
MIDI signals Renoise should "listen to". "Note Off" is the signal of a tone being cut,
"PrgChanges" are signals of changes of MIDI banks, programs etc., "Velocity" stands
for the impact with which the key on the keyboard was hit, and "Controller" represents
MIDI Controller messages.MIDIClock Slave Settings
In Device
The MIDI In Device handles all incoming MIDI signals.
The list of available MIDI Out Devices is created during the startup
of Renoise. Choose your favorite one here.Offset
Offset is the amount of time added or subtracted from the
time values of the MIDI signals this device/driver handles. Adding
or subtracting time to/from MIDI signals can be useful to compensate
delay of machines or such that results in heavy signal transfer.Thru
This setting defines if there should be a MIDI Thru Device/
driver, and if so, which one.
MIDIClock Master Settings
Out Device
The MIDI Out Device handles all outgoing MIDI signals.
The list of available MIDI Out Devices is created during the startup
of Renoise. Choose your favorite one here.Offset
Like withClock
Toggles if Renoise sends Master Clock MIDI messages.Start/Stop
If enabled, Renoise sends MIDI Start/Stop messages to
other devices. Use this if you have a MIDI Slave sequencer.SPP (Song Position Pointer)
Toggle this if you want to send out
Song Position Pointers while moving to a different song position in
RenoiseMMC (MIDI Machine Control)
MMC uses System Exclusive messages
("SysEx") - several specific SysEx messages were defined in order
to implement MMC to send messages such as start, stop or continue
to MIDI Devices.
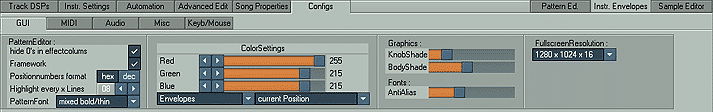
Audio
Autoplay Samples after loading
Defines whether or not a sample is
played after loading it into the Instruments editor.Autoplay Song after loading
Defines whether or not a song is
played after loading.Autosave Backup
IF Renoise crashes, it tries to save the current song.
This option though additionally gives you the possibility to save the current
song every X minutes.
CPU Usage
Provides a way to optimize CPU usage on slower CPUs as Renoise
program can be very CPU intensive. If you have a slower machine you can lower
this value but beware, it will lower audio quality! Check Requirements for
other CPU optimizations before you do this.
Device type/device - Direct Sound or ASIO
If using ASIO your sound card
must support it and your drivers must be properly installed. If you don't
have ASIO, select Direct Sound which is not as good as ASIO but works on
most audio cards. The latest DirectX version should be installed though.
If you don't know what ASIO is, look it up in the
Glossary section.Outlatency in ms / Samplerate
Latency
should be as small as possible to give a smaller "gap" before sounds start
playing when a key is pressed. However, if it is too small and your CPU or
operating system cannot handle it, it may sound "broken" and you will have
to increase the latency. Frequency also decreases CPU usage but don't go
below 22050 Hz because sound quality drops rapidly. However, all rates
supported by your audio card will be listed here. 44100 is CD quality sound,
48000 is DAT (digital audio tape) quality. If you wish very low latency
times solution is ASIO and/or fast CPU.Limit to stereo In/Out (only with ASIO configuration)
Some ASIO soundcards
have separate drivers for "stereo only" mode. Use this option to enable
this driver.Processing buffer size
Using lower values will give you (especially
with ASIO) lower audio latencies:
Use at least your audio latency/2 as process buffer size when using ASIO
to get a more stable and click free output. A smaller process buffer will
produce more CPU overhead (since the CPU has still to switch the buffers), so you should just try out settings that are
the best for your configuration. We recommend the setting of 128 samples
for ASIO and the setting of 512 samples for the Direct Sound.
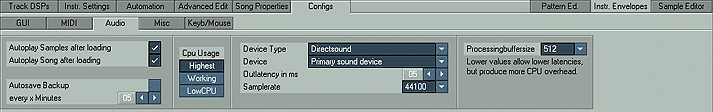
Misc (miscellaneous options)
Show track names in scopes
Sets what will be displayed on the track
scopes - track names or track numbersVST path
Click this button to choose your system's VST path.
Often it is "C:\Programs\Steinberg\Vstplugins". With the "Rescan" button
you can rescan your system's VST path to find new VST plugins. This can
be useful if you installed new ones while Renoise was running.Space Rec./Stop mode
In FastTracker2 mode Space toggles record mode
and stops song playback. In Renoise mode space only toggles playback of
song (use ESC to toggle edit/record mode in both modes).Default Trackmute mode
There are two ways Renoise can interpret a
"Mute" command you send. The first one is the (real) "Mute" way which
turns the sound of the channel down in the mixer. This mode will abruptly
"kill" all sound coming from this channel.
The second way is to interpret a "Mute" command of a track as a "Note Off"
command. This will result in the sound that the channel (with all its
effects and DSPs) makes with no more notes on the track played and (if
currently playing) the current note being halted. The second way doesn't
sound as harsh as the first one and will produce some "after mute sound".
Keyboard/Mouse
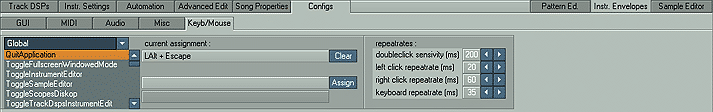
Shortcut names
These names represent the function you can define
keyboard shortcuts for."Current assignment" bar
This bar shows what keyboard shortcut is currently
assigned to the marked shortcut."New assignment" bar
The bar below the "Current assignment" bar shows
the new shortcut assignments you do.Clear/Assign
By clicking on "Clear", you delete the current shortcut
assignment for the marked shortcut. By clicking on "Assign", you change a
current shortcut to a new one displayed in the "New assignment" bar or
(if there was not assignment for this shortcut) create it as new one.
Repeatrates
Doubleclick sensitivity (ms)
Defines how fast two mouse
clicks have to come after each other to be interpreted as
a "double click" by Renoise.Left click repeatrate (ms)
Defines how long you have
to press the left mouse button to retrigger it continuously.Left click repeatrate (ms)
Defines how long you have
to press the right mouse button to retrigger it continuously.Keyboard repeatrate (ms)
Defines how long you have
to press a key on the computer keyboard to retrigger it continuously.
Back to the top!